Cash Management Cloud Platform
Cloud Platform
Problem & Solution
The Challenge: Shop owners managing multiple locations face significant operational challenges: they lack centralized visibility into cash transactions across all shops, making it impossible to monitor cash flow, detect anomalies, or make data-driven decisions. Employee management is fragmented across locations, with no unified system to assign roles, track permissions, or maintain accountability. Cash machine inventory and status monitoring requires manual checks at each location, leading to delayed responses to hardware issues. Without a centralized platform, shop owners cannot compare performance across locations, identify best practices, or detect fraudulent activities. Additionally, local systems need secure API authentication, but managing API keys and access control across multiple shops becomes a security and operational nightmare without a unified management system.
The Solution: I architected and built a centralized cloud-based dashboard platform that serves as the command center for multi-shop cash management operations. The platform integrates seamlessly with Cash Management Local System installations across all shop locations, aggregating transaction data, cash inventory, and operational metrics in real-time. Shop owners can manage employees and roles across all locations from a single interface, assign permissions granularly, and monitor cash machine status and inventory remotely. The platform provides comprehensive transaction tracking with up to 3 months of historical data, including detailed cash input/output records with denomination-level breakdowns. REST APIs enable local systems to authenticate securely using managed API keys, while JWT-based authentication ensures secure access for both API clients and web dashboard users. Hosted on cloud infrastructure with PM2 for process management and MongoDB as a service, the platform ensures high availability, scalability, and reliable data persistence. This centralized approach transforms multi-shop management from a fragmented challenge into a streamlined, data-driven operation.
Key Features & Business Impact
- Centralized employee and user management for all shop locations with unified account administration
- Comprehensive role-based access control (RBAC) allowing granular permission assignment for each employee across different shops
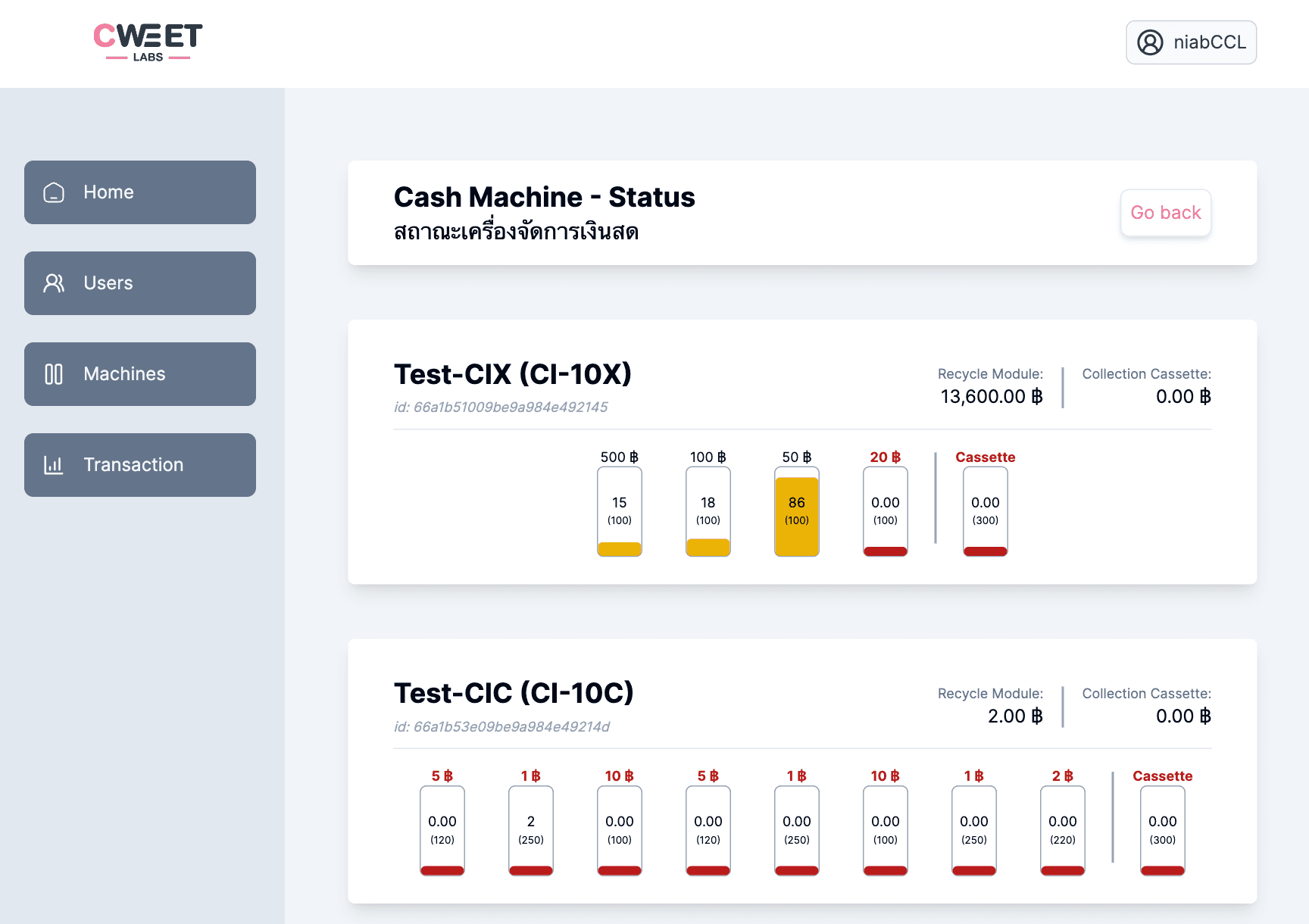
- Cash Infinity Machine management with real-time status monitoring, inventory tracking, and hardware health alerts
- API key management system for secure authentication of local systems, with key rotation and revocation capabilities
- RESTful API architecture enabling local systems to synchronize transactions, authenticate, and retrieve configuration data
- Extended transaction history tracking up to 3 months with complete audit trails for cash operations
- Detailed cash input/output analytics showing transaction flows, machine deposits, and withdrawals with timestamp records
- Denomination-level transaction details displaying quantity and value breakdowns for each cash transaction, enabling precise cash flow analysis
Technical Deep Dive
System Architecture: Hybrid Cloud-Local Model
The Cweetlabs cloud platform is built on a microservices-oriented architecture, hosted on cloud infrastructure with high availability and horizontal scaling capabilities. The frontend dashboard is built with Next.js and TypeScript, providing a responsive, real-time interface for shop owners and administrators. The backend API is built with Node.js and Express, running under PM2 process management for automatic restarts, load balancing, and zero-downtime deployments. MongoDB Atlas serves as the database-as-a-service, providing automatic backups, replication, and global distribution. NGINX acts as a reverse proxy and load balancer, handling SSL termination, request routing, and static asset serving. The platform communicates with local systems via REST APIs over HTTPS, receiving transaction data, machine status updates, and configuration requests. WebSocket connections enable real-time dashboard updates when transactions occur at any connected shop. This architecture ensures the platform can scale to support hundreds of shops and thousands of concurrent users while maintaining sub-second response times for dashboard interactions.
Authentication & Authorization (OAuth + RBAC)
Authentication is implemented using JWT (JSON Web Token) tokens for both API access and user sessions. When local systems authenticate, they use API keys managed through the dashboard, which are validated against the database. Upon successful authentication, the system issues a JWT token containing the system identifier, shop association, and permissions. For web dashboard users, login credentials are verified against MongoDB, and a JWT token is issued with user ID, role, and shop access permissions. JWT tokens include expiration times and are refreshed automatically before expiry. The system implements role-based access control (RBAC) at the API level, with middleware that validates user roles and permissions before processing requests. Shop owners have full access to all their shops, while employees are restricted to their assigned shops and permitted operations. API keys can be rotated, revoked, or regenerated through the dashboard, with immediate effect across all connected systems. This multi-layered authentication ensures that only authorized systems and users can access sensitive cash management data.
Real-Time Data Pipeline & Consistency
The data pipeline is designed to handle high-volume transaction data from multiple local systems simultaneously. When local systems synchronize data, they send batches of transactions via REST API endpoints. Each transaction is validated for completeness, checked for duplicates using idempotency keys, and inserted into MongoDB with proper indexing. The pipeline processes transactions asynchronously, allowing the API to respond quickly to local systems while background workers handle data aggregation and analytics computation. Real-time aggregation jobs update dashboard metrics (total cash, transaction counts, machine status) as new data arrives, ensuring shop owners always see current information. For historical data retention, the system maintains transaction records for 3 months, with automatic archival of older data to cost-effective storage. The pipeline implements retry logic for failed operations, dead-letter queues for problematic transactions, and monitoring alerts for pipeline health. WebSocket connections push real-time updates to connected dashboard clients when transactions occur, eliminating the need for manual page refreshes. This design ensures data consistency, minimizes latency, and provides reliable real-time visibility across all shop locations.
Database & Performance Optimization
The MongoDB database schema is optimized for multi-shop operations and analytical queries. Shops, users, and machines are stored in separate collections with proper indexing on frequently queried fields (shop_id, user_id, machine_id). Transaction collections use compound indexes on (shop_id, created_at) for efficient time-range queries and (machine_id, transaction_type, created_at) for machine-specific analytics. Denomination-level transaction details are stored as nested documents within transaction records, enabling fast queries without joins. For dashboard performance, materialized views (implemented as MongoDB aggregation pipelines) pre-compute daily and monthly summaries (total cash per shop, transaction counts, cash flow trends) and store them in summary collections. These summaries are updated incrementally as new transactions arrive, ensuring dashboard queries complete in milliseconds even with months of historical data. Connection pooling via MongoDB driver settings ensures efficient database connection management under high concurrent load. Query optimization focuses on index usage, projection to limit data transfer, and aggregation pipelines for complex analytics. The schema supports horizontal scaling through MongoDB sharding, allowing the platform to handle growing numbers of shops and transactions without performance degradation. TTL indexes automatically expire old transaction data after 3 months, maintaining database size while preserving analytical summaries.
Technology Stack
 NextJS
NextJS Typescript
Typescript TailwindCSS
TailwindCSS MongoDB
MongoDB NGINX
NGINX PM2
PM2