Auto Transfer Payment System
Payment & Security
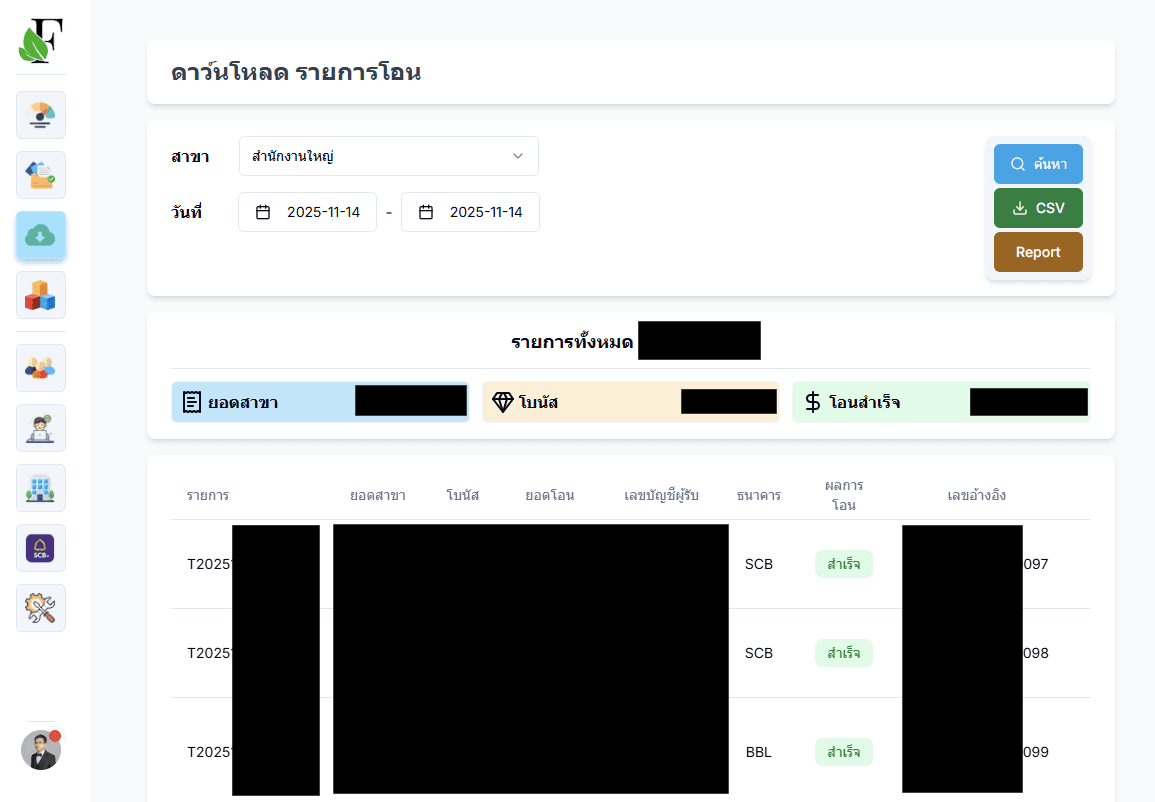
Problem & Solution
The Challenge: Shop owners managing agricultural product purchasing processes face significant operational challenges: they must constantly monitor and manually approve cash transfer requests from employees across multiple branch locations, requiring extensive communication and time-consuming validation of transfer amounts. This manual process creates risks of human error, incorrect transfer amounts, and delayed payments that can disrupt supplier relationships. The lack of centralized transfer management means owners cannot efficiently track payment history, validate bank account information, or maintain proper audit trails. Additionally, the process of downloading and processing transfer reports from banking partners like SCB requires manual SFTP operations, further increasing operational overhead and potential for errors.
The Solution: I designed and built a high-security automated transfer payment system as an integrated feature of the FPN-CRM System, centralizing and automating all transfer payments for agricultural product purchasing processes. The system manages member bank account information with a document request and approval workflow that requires authorization before any modifications can be made. Short-lived JWT-based authentication ensures secure access, while multiple validation layers (shop token, operation token) prevent unauthorized transfers. The system only allows transfers to active members, ensuring data integrity and preventing payments to inactive or invalid accounts. Seamless integration with SCB Partner Application enables real-time transfer processing, and the system encapsulates the SFTP file download process, allowing users to select and download SCB reports with a single click. Built with a microservices-oriented architecture and PM2 for process management, the system handles transfer requests from multiple branch sites in real-time, eliminating manual intervention and significantly reducing the risk of errors.
Key Features & Business Impact
- Comprehensive member information management with secure bank account data storage and validation
- Document request and approval system requiring authorization before any member information modifications, ensuring data integrity and audit compliance
- Short-lived JWT-based authentication with automatic token expiration and refresh mechanisms for enhanced security
- Multi-layer validation system requiring both shop token and operation token before processing any transfer, preventing unauthorized transactions
- Active member validation that only allows transfers to verified, active members, preventing payments to inactive or invalid accounts
- Seamless integration with SCB Partner Application for secure, real-time transfer processing
- One-click SFTP report download functionality that encapsulates complex file transfer processes, allowing users to easily select and download SCB transfer reports
Technical Deep Dive
System Architecture: Hybrid Cloud-Local Model
The Auto Transfer Payment System is built on a microservices-oriented architecture with clear separation of concerns, integrated as a feature module within the FPN-CRM System. The architecture consists of multiple independent services: a member management service handling bank account information, a transfer processing service managing payment workflows, an approval workflow service for document requests, and an integration service for SCB Partner Application communication. Each service operates independently and communicates via REST APIs with JWT authentication. PM2 process management ensures high availability, automatic restarts on failures, load balancing across multiple instances, and zero-downtime deployments. The system uses the same technology stack as FPN-CRM (Next.js, TypeScript, PostgreSQL, Drizzle ORM) for consistency and code reuse. The microservices architecture allows each component to scale independently based on load, with the transfer processing service able to handle high-volume requests from multiple branch sites simultaneously. This separation of concerns ensures that security vulnerabilities in one service don't compromise the entire system, and updates can be deployed to individual services without affecting others.
Authentication & Authorization (OAuth + RBAC)
Authentication is implemented using short-lived JWT tokens with automatic expiration and refresh mechanisms. When users authenticate, they receive a JWT token with a short expiration time (typically 15-30 minutes) that includes user ID, role, permissions, and shop association. Before the token expires, the system automatically refreshes it using a refresh token stored securely. For transfer operations, the system implements multi-token validation: each transfer request must include both a shop token (validating the requesting shop's identity) and an operation token (validating the specific operation's authorization). These tokens are validated independently, and both must be valid for the transfer to proceed. The system maintains a token blacklist for revoked tokens, ensuring that compromised tokens cannot be used even if they haven't expired. All authentication events are logged for audit purposes, including login attempts, token refreshes, and failed validations. This multi-layered authentication approach ensures that even if one token is compromised, the additional validation layers prevent unauthorized access.
Real-Time Data Pipeline & Consistency
The data pipeline is designed to handle transfer requests from multiple branch sites in real-time while maintaining security and data integrity. When a transfer request is initiated from a branch, it first goes through validation: member status check (must be active), bank account verification, amount validation, and multi-token authentication. Once validated, the request is queued for processing. The transfer processing service retrieves the request, validates it again against current member data, and initiates the transfer through the SCB Partner Application API. The system maintains real-time communication with SCB's API, receiving immediate confirmation of transfer status (success, failure, pending). All transfer transactions are logged with complete audit trails including timestamps, user IDs, shop IDs, member information, amounts, and status. For reporting, the system periodically connects to SCB's SFTP server to download transfer reports. The SFTP process is encapsulated in a background service that handles authentication, file listing, selection, and download automatically. Users can trigger report downloads through the dashboard with a single click, and the system handles all the complex SFTP operations transparently. The pipeline implements retry logic for failed transfers, dead-letter queues for problematic requests, and real-time status updates to connected dashboard clients via WebSocket connections.
Database & Performance Optimization
The database schema is optimized for high-performance user and bank account query operations, which are critical for transfer processing. Member information and bank account data are stored in normalized tables with strategic indexes on frequently queried fields. Composite indexes on (member_id, status) enable fast active member lookups, while indexes on (shop_id, member_id) optimize queries for shop-specific member lists. Bank account information is indexed on account_number and bank_code for rapid validation during transfer processing. The system implements query optimization techniques including selective column projection (only fetching required fields), connection pooling via Drizzle ORM to manage database connections efficiently, and prepared statements to prevent SQL injection while improving query performance. For transfer history queries, materialized views pre-compute daily and monthly summaries (total transfers per shop, success rates, average amounts) and are refreshed incrementally. The schema includes check constraints to enforce data validation rules (e.g., transfer amounts must be positive, account numbers must match format requirements). Query execution plans are monitored and optimized using EXPLAIN ANALYZE to identify and eliminate slow queries. The database design supports high-concurrency scenarios where multiple branch sites may query member information simultaneously, with row-level locking to prevent data conflicts during updates. This optimization ensures that transfer processing remains fast even under high load from multiple branch sites.
Technology Stack
 NextJS
NextJS Typescript
Typescript TailwindCSS
TailwindCSS PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL Drizzle ORM
Drizzle ORM PM2
PM2